Modbus connection parameters
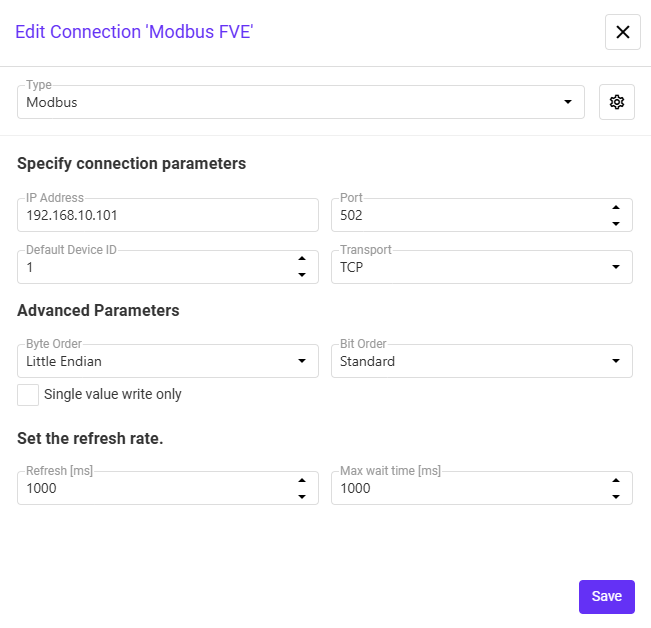
- Byte Order:
- Little Endian
- The least significant byte is stored first (e.g.
0x1234→34 12)
- The least significant byte is stored first (e.g.
- Big Endian
- The most significant byte is stored first (e.g.
0x1234→12 34)
- The most significant byte is stored first (e.g.
- Little Endian
- Bit Order:
- Standard
- Bits are ordered from the most significant bit (bit 7) to the least significant bit (bit 0).
Example:0b10000000→ bit 7 is1, bit 0 is0.
- Bits are ordered from the most significant bit (bit 7) to the least significant bit (bit 0).
- Reverse
- Bits are ordered from the least significant bit (bit 0) to the most significant bit (bit 7).
Example:0b10000000→ bit 0 is1, bit 7 is0.
- Bits are ordered from the least significant bit (bit 0) to the most significant bit (bit 7).
- Standard
- Single value write only:
- This option switches between multiple write class and single write class
- Max wait time
- Specifies max wait time to receive value – the time for which will DataTalk wait for response from PLC adjust this according to your network speed and PLC capatabilities
FC5 “Force Single Coil” & FC6 “Preset Single Register” X FC15 “Force Multiple Coil” & FC16 “Preset Multiple Registers”
Address mapping
In our system, we use a short or symbolic addressing format to simplify working with Modbus registers. For example:
- H:0 refers to Modbus address 40001
- H:1 = 40002, H:7 = 40008, etc.
| Type | Modicon Address Range | Access | Short Address Prefix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discrete Outputs (Coils) | 00001–09999 | Read / Write | O: (Output) | O:0 → 00001 |
| Discrete Inputs | 10001–19999 | Read-only | I: (Input) | I:0 → 10001 |
| Input Registers | 30001–39999 | Read-only | R: (Register/Input) | R:0 → 30001 |
| Holding Registers | 40001–49999 | Read / Write | H: (Holding) | H:0 → 40001 |
Currently our Modbus communication protocol doesn’t support string read / write only numerical values
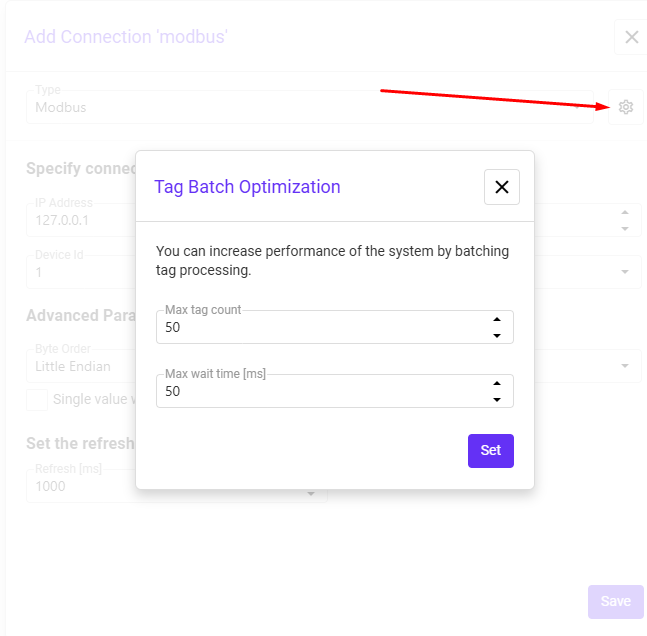
Batch optimization
Batch optimization means grouping multiple tags into a single Modbus request instead of reading or writing them one by one. This improves performance by reducing the number of requests, lowering communication overhead, and making data exchange faster.
- Max tag count – the maximum number of tags that can be grouped into one request.
- Max wait time [ms] – maximum time the system will wait to collect tags before sending the batch.
In short: larger batches = fewer requests and better efficiency, but possibly slightly slower response for individual tags.
Device ID: Device ID can be changed in the address section in the tags database –
Example: If you have four power meters on the same line, you assign IDs like 1, 2, 3, and 4.