To enable data forwarding from DataTalk to external platforms, the OT/IT Gateway must first be configured and linked with selected tags in the project. The setup defines where, when, and how the data will be published to third-party systems.
Key Steps & Features
- Creating a Gateway
- In the project tree, create a new gateway and assign it a name.
- In the top menu of the gateway settings, choose the gateway type, which refers to the destination platform or service (e.g., AWS, Azure, SQL database, REST API).
- Important: One gateway instance corresponds to one target service. If data needs to be sent to multiple platforms, separate gateways must be created for each.
- Defining Execution Triggers (Publishing Logic)
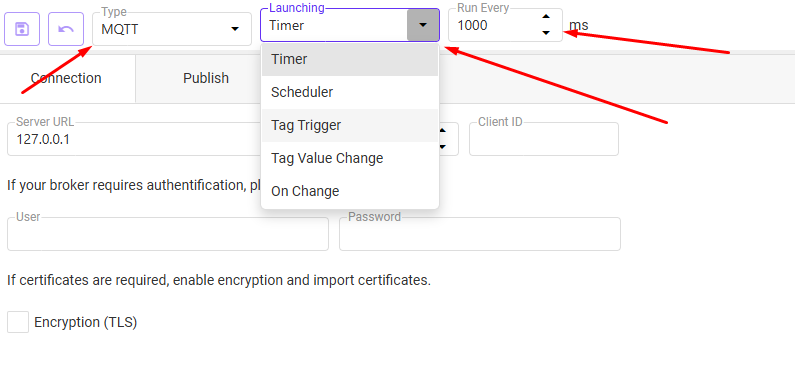
- The trigger type determines when data should be sent:
- Timer:
Sends data at a regular time interval (e.g., every 1000 ms = every second). - Scheduler:
Sends data at a specific time (e.g., every day at midnight). - Tag Trigger:
Sends data when a specific tag reaches a defined value.
Example: When a machine status tag changes to “1” (start), data is sent. - Tag Value Change:
Sends data any time the value of a selected tag changes, regardless of the new value. - On Change:
???
- Timer:
- The trigger type determines when data should be sent:
- Platform Authentication
- After selecting the platform type, fill in the connection credentials (e.g., API keys, server URLs, tokens).
- Once completed, the gateway is active and ready to forward data.
- Detailed connection guides are available in the “Publish Platforms” section.
Assigning Tags to a Gateway
- Navigate to the Tag Database.
- Select the tag(s) you wish to publish.
- In the “Gateway” column, check the box to open a list of available gateways created in the project.
- You can assign one tag to multiple gateways simultaneously.
Example: A single tag can be configured to publish its value to both Amazon AWS and a custom REST API endpoint.
The OT/IT Gateway setup enables scalable, flexible, and event-driven data integration between DataTalk and external systems—making it a critical component for real-time analytics, cross-system communication, and cloud-based infrastructure.